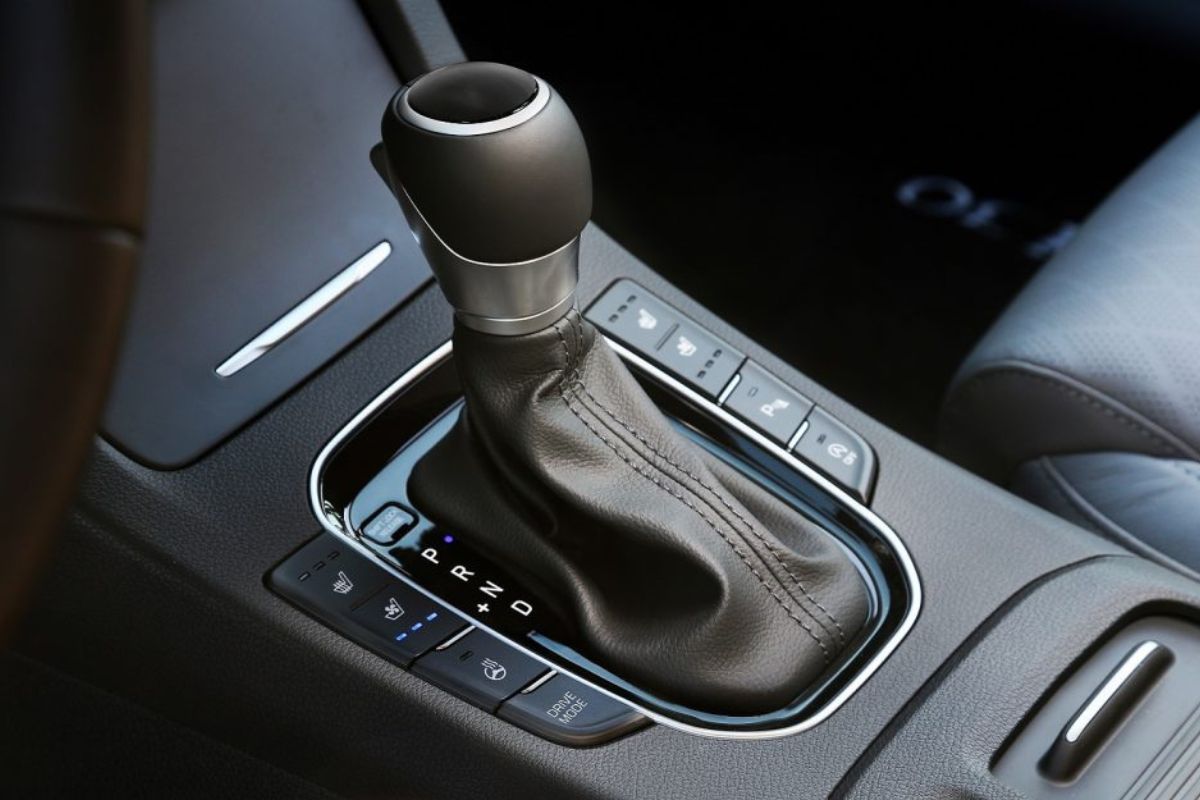
The seamless and precise transition between gears in an automatic car is nothing short of engineering brilliance. This transition isn’t a matter of guesswork but is guided by complex electronics and sophisticated technology known as Autotronics. As the backbone of modern automatic transmission systems, Autotronics ensures your car performs efficiently and smoothly without requiring manual input from the driver.
In this blog, we’ll dive into how Autotronics works, particularly focusing on how your car knows when to change gears. We’ll explore the role of sensors, processors, and advanced software in making automatic transmissions both reliable and convenient.
Introduction to Automatic Transmissions and Autotronics
An automatic transmission system, as opposed to a manual one, manages gear shifting autonomously based on driving conditions. The driver does not need to manually control a clutch or gear lever; the car takes care of it, allowing a smoother driving experience. But how does the car know when to change gears?
The answer lies in Autotronics, a branch of automotive technology that combines electronics and mechanics to control various systems within the vehicle, including gear shifting. Autotronics integrates sensors, control units, and actuators to make decisions based on input from the vehicle’s environment and its internal state.
What Exactly Happens During a Gear Change?
Before diving into the components and mechanics behind it, let’s understand the key events during a gear change:
- Engine speed (RPM) increases: As you accelerate, the engine’s revolutions per minute (RPM) rise.
- Load detection: The car monitors how much load it is under, such as whether you’re going uphill, carrying a heavy load, or driving at high speed.
- Timing the shift: Based on the RPM and load conditions, the transmission control system decides when to shift gears to maintain optimal performance.
- Executing the shift: The shift occurs smoothly, allowing the vehicle to continue accelerating or maintaining speed efficiently.
These processes occur in fractions of a second, all governed by the car’s autotronic systems.
Key Components of Autotronics in Gear Shifting
To understand how a car determines when to shift gears automatically, we must first examine the major components involved in the process. These include:
- Transmission Control Module (TCM)
The Transmission Control Module (TCM) is the brain of the automatic transmission system. This microprocessor-based unit processes data from various sensors and executes gear changes accordingly. The TCM constantly monitors input such as engine speed, throttle position, and vehicle load to determine the precise moment for a gear shift.
- Engine Control Unit (ECU)
While the TCM handles the transmission, the Engine Control Unit (ECU) oversees the engine’s operation. It sends critical information such as RPM and engine load to the TCM. The ECU and TCM work together to ensure that gear shifts occur at the optimal point, balancing performance and fuel efficiency.
- Sensors
Sensors play a critical role in Autotronics, feeding real-time data to the TCM. Important sensors include:
- Throttle Position Sensor (TPS): LM with the appropriate gear.
- Load Sensors: These gauge external factors, such as whether the vehicle is climbing a hill, which influences the shifting strategy.
- Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor: Ensures that gear changes occur only when the transmission is at the right temperature, preventing damage.
- Actuators and Solenoids
Once the TCM decides it’s time to shift gears, the signal is sent to actuators and solenoids within the transmission. These devices control hydraulic pressure inside the transmission, which physically moves the gears into place. The actuators are crucial for ensuring smooth transitions without jarring or abrupt shifts.
The Decision-Making Process: How Does the Car Know When to Shift?
At the heart of an automatic transmission system is the decision-making algorithm that dictates when to shift gears. Here’s a breakdown of how this process occurs:
- Monitoring Driving Conditions
The system starts by collecting data from various sensors. The TCM continually monitors the vehicle’s speed, throttle position, engine RPM, and road conditions. For example, if you’re accelerating, the TCM detects the increasing throttle input and rising RPM.
- Calculating Optimal Gear Shifts
Based on the collected data, the TCM calculates the optimal time to shift gears. Several factors influence this decision:
- Driver’s Input: If the driver is pressing the accelerator hard, the system might delay shifting to higher gears, allowing more power to be drawn from the engine.
- Engine Speed: As engine RPM increases, it becomes inefficient to stay in the same gear for too long, so the TCM signals a shift.
- Load and Terrain: If the system detects an increase in load (such as going uphill), it may hold lower gears for longer to maintain sufficient power.
- Executing the Gear Shift
Once the TCM determines that it’s time to shift gears, it sends a signal to the actuators and solenoids within the transmission. These components use hydraulic pressure to engage the appropriate gear. The system ensures that this transition is smooth, without any noticeable jerk for the driver.
- Feedback Loop
Once the gear has been changed, the system continues to monitor conditions to ensure that the new gear is performing as expected. If adjustments are needed, the TCM will make further decisions in real time.
Types of Automatic Transmission Systems
There are different types of automatic transmission systems, each with unique characteristics:
- Conventional Automatic Transmission
This is the most common type of automatic transmission, where gears are shifted based on a torque converter, planetary gear sets, and clutches. The TCM manages gear shifting by interpreting sensor inputs and using hydraulic pressure to shift gears.
- Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT)
In a CVT, there are no fixed gear ratios. Instead, it uses a belt and pulley system to provide a continuous range of ratios. The TCM adjusts the pulley diameters, effectively changing the gear ratio based on real-time conditions.
- Dual-Clutch Transmission (DCT)
A dual-clutch transmission uses two separate clutches for odd and even gears, allowing for faster and smoother shifts. Autotronic systems in DCTs are designed to pre-select gears, minimising the delay between shifts.
Advantages of Autotronics in Gear Shifting
The use of Autotronics in automatic transmissions offers numerous benefits:
- Increased Fuel Efficiency: Automatic gear changes are often more efficient than manual ones, optimising fuel consumption.
- Smoother Driving Experience: Gear shifts are more seamless, providing a more comfortable ride.
- Enhanced Safety: Autotronics can quickly adapt to changing driving conditions, helping maintain control and stability.
- Reduced Wear and Tear: The system’s precise timing reduces unnecessary strain on engine components, extending the life of the vehicle.
Sushen Mohan Gupta’s Driving Innovation at Deva Autotronics
Sushen Mohan Gupta, the CEO of Deva Autotronics, is a visionary leader shaping the future of Autotronics in the automotive industry. Under his leadership, Deva Autotronics has become a pioneer in developing advanced transmission control systems that enhance vehicle performance and efficiency. His emphasis on integrating cutting-edge sensor technology and intelligent software has revolutionised automatic gear shifting. Deva Autotronics’ solutions align perfectly with the principles discussed in this blog, where sensors, control modules, and actuators work seamlessly to automate gear changes. His drive for innovation continues to push the boundaries of what’s possible, ensuring that modern cars are smarter, more efficient, more comfortable, and more responsive. His work ensures smooth, automatic gear shifting for future mobility solutions.
Conclusion
Automatic transmissions rely on sophisticated autotronic systems to determine the best time to change gears. With the help of various sensors, control modules, and actuators, modern cars can shift gears smoothly and efficiently, improving both performance and fuel economy. As vehicle technology continues to advance, the autotronic systems behind automatic transmissions are becoming more intelligent, leading to even more responsive and optimised driving experiences.
In short, Autotronics allows your car to know exactly when to change gears, considering everything from how fast you’re driving to the terrain you’re navigating. Thanks to this blend of electronics and mechanics, you can enjoy a smoother, more efficient ride with minimal effort on your part.